Saturday, February 02, 2013
Candlemas Day, 2013
Candlemas Day
by Robert Herrick
Kindle the Christmas brand, and then
Till sunset let it burn;
Which quench'd then lay it up again
Till Christmas next return.
Part must be kept wherewith to tend
The Christmas log next year;
And where 'tis safely kept, the fiend
Can do no mischief there.
This poem describes the custom of taking down the last of the Christmas holly on Candlemas, and burning it. It should certainly be dry enough by now.
However, an alternate custom was to reserve the last of the holly and use it as kindling for the fire for the Shrove Tuesday pancakes. This year, that would mean keeping the dried-out holly around almost another 3 weeks.
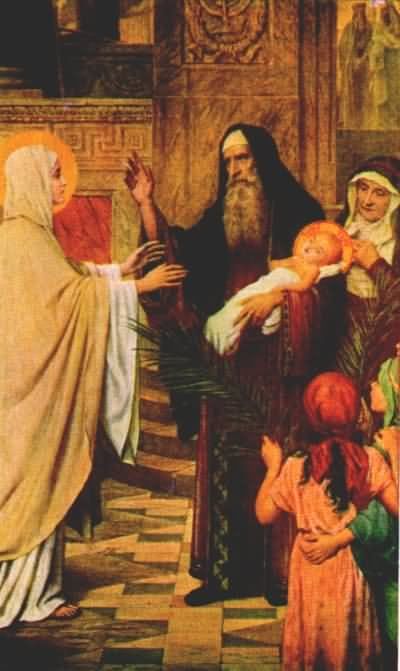
This is the feast of the Purification of the Virgin, which, under Jewish Law comes 40 days after childbirth. And Candlemas is 40 days after Christmas. The Church also (rather oddly, I think) adds the Feast of the Presentation. Odd, because under Jewish Law, the baby Jesus would have been presented and circumcised on the eighth day after his birth, or the Octave of Christmas. So, there were two Temple-related events after the Nativity, the Presentation on January 1st, and the Purification or Churching of Mary, on February 2nd. The Holy Family must have remained in Bethlehem (though they probably moved out of the stable, as the Magi story speaks of a "house") to be close to Jerusalem and the Temple for these two events. It can only be after this that the Flight to Egypt and the Slaughter of the Holy Innocents took place.
How did Candlemas get its name? Today was the day to bring to church for blessing the year's supply of candles, especially candles with a semi-sacramental nature, like the candles placed in the window on Christmas Eve, Christmas Day, New Years, and Epiphany in Irish homes, candles for the Advent wreath, candles for the home sick visit kit, or candles used in home shrines.
One of the European superstitions connected with Candlemas was that a fair, clear Candlemas meant a longer winter, where a cloudy Candlemas would mean the end of winter was at hand. In Europe, the end of February is often quite spring-like, where here in the US (especially here in New England), it tends to be more wintery, as our seasons run about 3 weeks behind the European seasons.
Here is a German saying:
When it storms and snows on Candlemas Day,
Spring is not far away;
if it's bright and clear,
Spring is not yet near.
This gave rise to the legend that if the groundhog sees his shadow on February 2nd (now better known as Groundhog Day) it means 6 more weeks of winter (as opposed to only 4 more weeks if he does not see it).
Check out our friends at Fish Eaters for more on Candlemas customs.
Also, see The Golden Legend on the Purification of Our Blessed Lady.
by Robert Herrick
Kindle the Christmas brand, and then
Till sunset let it burn;
Which quench'd then lay it up again
Till Christmas next return.
Part must be kept wherewith to tend
The Christmas log next year;
And where 'tis safely kept, the fiend
Can do no mischief there.
This poem describes the custom of taking down the last of the Christmas holly on Candlemas, and burning it. It should certainly be dry enough by now.
However, an alternate custom was to reserve the last of the holly and use it as kindling for the fire for the Shrove Tuesday pancakes. This year, that would mean keeping the dried-out holly around almost another 3 weeks.
This is the feast of the Purification of the Virgin, which, under Jewish Law comes 40 days after childbirth. And Candlemas is 40 days after Christmas. The Church also (rather oddly, I think) adds the Feast of the Presentation. Odd, because under Jewish Law, the baby Jesus would have been presented and circumcised on the eighth day after his birth, or the Octave of Christmas. So, there were two Temple-related events after the Nativity, the Presentation on January 1st, and the Purification or Churching of Mary, on February 2nd. The Holy Family must have remained in Bethlehem (though they probably moved out of the stable, as the Magi story speaks of a "house") to be close to Jerusalem and the Temple for these two events. It can only be after this that the Flight to Egypt and the Slaughter of the Holy Innocents took place.
How did Candlemas get its name? Today was the day to bring to church for blessing the year's supply of candles, especially candles with a semi-sacramental nature, like the candles placed in the window on Christmas Eve, Christmas Day, New Years, and Epiphany in Irish homes, candles for the Advent wreath, candles for the home sick visit kit, or candles used in home shrines.
One of the European superstitions connected with Candlemas was that a fair, clear Candlemas meant a longer winter, where a cloudy Candlemas would mean the end of winter was at hand. In Europe, the end of February is often quite spring-like, where here in the US (especially here in New England), it tends to be more wintery, as our seasons run about 3 weeks behind the European seasons.
Here is a German saying:
When it storms and snows on Candlemas Day,
Spring is not far away;
if it's bright and clear,
Spring is not yet near.
This gave rise to the legend that if the groundhog sees his shadow on February 2nd (now better known as Groundhog Day) it means 6 more weeks of winter (as opposed to only 4 more weeks if he does not see it).
Check out our friends at Fish Eaters for more on Candlemas customs.
Also, see The Golden Legend on the Purification of Our Blessed Lady.
Friday, February 01, 2013
Saint Brigid Of Kildare

Here is a website on the beloved patroness of Ireland.
Included on a page, are 3 different methods for making a St. Brigid's Cross. I notice that the website has been moved since the last year, and the link for the directions on how to make the cross are now either not working accidentally, or deliberately omitted to get people to buy a book with the directions. I always wanted to try making this type of cross, but I doubt my skills at that sort of thing are equal to the task.

Interestingly. on another page of the site (scroll down, but take the time to peruse the entire page of seasonal customs, much of the information derived from the excellent The Year In Ireland by Kevin Danaher), there is yet another Luck Visit custom associated with St. Brigid's Eve.
In my various researches, I have come across numerous luck visit rituals (mostly) from the British Isles, and mostly associated with what we now call "the holidays," the period from Halloween through Candlemas. To jog the memory, I have discussed here Soulling, Trick-or-Treat, A Penny For the Guy, Something For Thanksgiving (apparently entirely American, though derived from British precedents), wassailling, carolling, John Canoe (again American, and particular to the slave population on Southern plantations), and the Plough Monday Ritual and play.
Irish folk used to go about with an effigy of Saint Brigid dressed in white, and offer this song in exchange for a gift of food, drink, or coin:
Something for poor Biddy!
Her clothes are torn
Her shoes are worn
Something for poor Biddy!
or
Here is Brigid dressed in white,
Give her a penny for her night
She is deaf, she is dumb
She cannot talk without a tongue.
or
Here comes Brigid dressed in white
Give her something for the night
She is deaf, she is dumb
For Gods sake give her some.
Note that among the Celts, and in Europe generally, February 1st is considered the beginning of Spring, where here in the Northeastern US, it is very much a cold, snowy winter month, with the first real hope for nice weather at least 6 weeks off, often longer.
But take heart! St. Brigid is our patroness, and her feast this year falls squarely during Carnival. So we can celebrate our Irishness with our patroness today!
Friday At the Foot Of the Cross
i. O my Lord Jesus Christ crucified, Son of the most Blessed Virgin Mary, open Thy ears, and listen to me as Thou didst listen to Thy eternal Father upon Mount Tabor.
Say then a Credo.
ii. O my Lord Jesus Christ crucified, Son of the most Blessed Virgin Mary, open Thine eyes, and look upon me as Thou didst look from the tree of the Cross upon Thy dear Mother sorrowing and afflicted.
Credo.
iii. O my Lord Jesus Christ crucified, Son of the most Blessed Virgin Mary, open Thy blessed mouth, and speak as Thou didst speak to St. John when Thou gavest him for son to Thine own most beloved Mother.
Credo.
iv. O my Lord Jesus Christ crucified, Son of the most Blessed Virgin Mary, open Thine arms, and embrace me as Thou didst open them upon the Cross to embrace the whole human race.
Credo.
v. O my Lord Jesus Christ crucified, Son of the Blessed Virgin Mary, open Thy Heart, and receive therein my heart, and hear me in all that I ask of Thee, if so be it be agreeable to Thy most holy will.
Credo.
Thursday, January 31, 2013
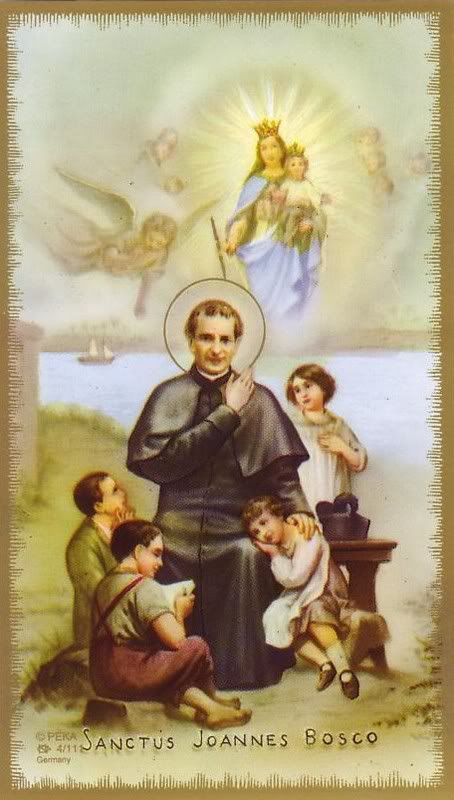
Saint John Bosco
Tuesday, January 29, 2013
Saint Francis de Sales, Bishop, Confessor, & Doctor Of the Church

Here is a brief biography of this great saint of the Counter Reformation and Doctor of the Church.
His An Introduction To the Devout Life, which I read for the first time last year, is a Catholic classic. Here it is in e-text.
You don't really need that St. John's Wort.
One of the principle effects of holy abandonment in God is evenness of spirits in the various accidents of this life, which is certainly a point of great perfection, and very pleasing to God. The way to maintain it is in imitation of the pilots, to look continually at the Pole Star, that is, the Divine Will, in order to be constantly in conformity with it. For it is this will which, with infinite wisdom rightly distributes prosperity and adversity, health and sickness, riches and poverty, honor and contempt, knowledge and ignorance, and all that happens in this life. On the other hand, if we regard creatures without this relation to God, we cannot prevent our feelings and disposition from changing, according to the variety of accidents which occur.
Sunday, January 27, 2013
Septuagesima Sunday
The Mystery of Septuagesima
from Abbott Prosper Gueranger, The Liturgical Year
The season upon which we are now entering is expressive of several profound mysteries. But these mysteries belong not only to the three weeks which are prearatory to Lent: they continue throughout the whole period of time which separates us from the great feast of Easter.
The number seven is the basis of all these mysteries. We have already seen how the holy Church came to introduce the season of Septuagesima into her calendar. Let us now meditate on the doctrine hidden under the symbols of her liturgy. And first, let us listen to St. Augustine, who thus gives is the clue to the whole of our season's mysteries. 'There are two times,' says the holy Doctor: 'one which is now, and is spent in the temptations and tribulations of this life; the other which shall by then, and shall be spent in eternal security and joy. In figure of these, we celebrate two periods: the time before Easter, and the time after Easter. That which is before Easter signifies the sorrow of this present life; that which is after Easter, the blessedness of our future state... Hence it is that we spend the first in fasting and prayer; and in the second we give up our fasting, and give ourselves to praise.'
The Church, the intepreter of the sacred Scriptures, often speaks to us of two places, which correspond with these two times of St. Augustine. These two places are Babylon and Jerusalem. Babylon is the image of this world of sin, in the midst whereof the Christian has to spend his years of probation; Jerusalem is the heavenly country, where he is to repose after all his trials. The people of Israel, whose whole history is but one great type of the human race, was banished from Jerusalem and kept in bondage in Babylon.
Now, this captivity, which kept the Israelites exiles from Sion, lasted seventy years; and it is to express this mystery, as Alcuin, Amalarius, Ivo of Chartres, and all the great liturgists tell us, that the Church fixed the number of seventy for the days of expiation. It is true, there are but sixty-three days between Septuagesima and Easter; but the Church, according to the style so continually used in the sacred Scriptures, uses the round number instead of the literal and precise one.
The duration of the world itself, according to the ancient Christian tradition, is divided into seven ages. The human race must pass through the seven ages before the dawning of the day of eternal life. The first age included the time from the creation of Adam to Noah; the second begins with Noah and the renovation of the earth by the deluge, and ends with this the vocation of Abraham; the third opens with this first formation of God's chosen people, and continues as far as Moses, through whom God gave the Law; the fourth consists of the period between Moses and David, in whom the house of Juda received the kingly power; the fifth is formed of the years which passed between David's reign and the captivity of Babylon, inclusively; the sixth dates from the return of the Jews to Jerusalem, and takes us on as far as the birth of our Saviour. Then, finally, comes the seventh age; it starts with the rising of this merciful Redeemer, the Sun of justice, and is to continue till the dread coming of the Judge of the livng and the dead. These are the seven great divisions of time; after which, eternity.
In order to console us in the midst of the combats, which so thickly beset our path, the Church, like a beacon shining amidst the darkness of this our earthly abode, shows us another seven, which is to succeed the one we are now preparing to pass through. After the Septuagesima of mourning, we shall have the bright Easter with its seven weeks of gladness, foreshadowing the happiness and bliss of heaven. After having fasted with our Jesus, and suffered with Him, the day will come when we shall rise together with Him, and our hearts shall follow Him to the hightest heavesn; and then after a brief interval, we shall feel the Holy Ghost descending upon us, with His seven Gifts. The celebration of all these wondrous joys will take us seven weeks, as the great liturgists observe in their interpretation of the rites of the Church. The seven joyous weeks from Easter to Pentecost will not be too long for the future glad mysteries, which, after all, will be but figures of a still gladder future, the future of eternity.
Having heard these sweet whisperings of hope, let us now bravely face the realities brought before us by our dear mother the Church. We are sojourners upon this earth; we are exiles and captives in Babylon, that city which plots our ruin. If we love our country, if we long to return to it, we must be proof against the lying allurements of this strange land, and refuse the cup she proffers us, and with which she maddens so many of our fellow captives. She invites us to join in her feasts and her songs; but we must unstring our harps, and hang them on the willows that grow on her river's bank, till the signal be given for our return to Jerusalem. She will ask us to sing to her the melodies of our dear Sion: but how shall we, who are so far from home, have heart to 'sing the song of the Lord in a strange land'? No, there must be no sign that we are content to be in bondage, or we shall deserve to be slaves forever.
These are the sentiments wherewith the Church would inspire us during the penitential season which we are now beginning. She wishes us to reflect on the dangers that beset us; dangers which arise from ourselves and from creatures. During the rest of the year she loves to hear us chant the song of heavne, the sweet Alleluia; but now, she bids us close our lips to this word of joy, because we are in Babylon. We are pilgrims absent from our Lord, let us keep our glad hymn for the day of His return. We are sinners, and have but too often held fellowship with the world of God's enemies; let us become purified by repentance, for it is written that 'praise is unseemly in the mouth of a sinner.'
The leading feature, then, of Septuagesima, is the total suspension of the Alleluia, which is not to again be heard upon the earth until the arrival of that happy day, when having suffered death with our Jesus, and having been buried together with Him, we shall rise again with Him to a new life.
The sweet hymn of the angels, Gloria in excelsis Deo, which we have sung every Sunday since the birth of our Saviour in Bethlehem, is also taken from us; it is only on the feasts of the saints which may by kept during the week that we shall be allowed to repeat it. The night Office of the Sunday is to lose also, from now till Easter, its magnificent Ambrosian hymn, the Te Deum; and at the end of the holy Sacrifice, the deacon will no longer dismiss the faithful with his solemn Ite, Missa est, but will simply invite them to continue their prayers in silence, and bless the Lord, the God of mercy, who bears with us, notwithstanding all our sins.
After the Gradual of the Mass, instead of the thrice repeated Alleluia, which prepared our hearts to listen to the voice of God in the holy Gospel, we hsall hear but a mournful and protracted chant, called, on that account, the Tract.
That the eye, too, may teach us that the season we are entering on is one of mourning, the Church will vest her ministers (both on Sundays and on the days during the week which are not feasts of Saints) in the sombre purple. Until Ash Wednesday, however, she permits the deacon to wear his dalmatic, and the subdeacon his tunic; but from that day forward, they must lay aside these vestments of joy, for Lent will then have begun and our holy mother will inspire us with the deep spirit of penance, but suppressing everything of that glad pomp, which she loves at other seasons, to bring into the sanctuary of her God.
from Abbott Prosper Gueranger, The Liturgical Year
The season upon which we are now entering is expressive of several profound mysteries. But these mysteries belong not only to the three weeks which are prearatory to Lent: they continue throughout the whole period of time which separates us from the great feast of Easter.
The number seven is the basis of all these mysteries. We have already seen how the holy Church came to introduce the season of Septuagesima into her calendar. Let us now meditate on the doctrine hidden under the symbols of her liturgy. And first, let us listen to St. Augustine, who thus gives is the clue to the whole of our season's mysteries. 'There are two times,' says the holy Doctor: 'one which is now, and is spent in the temptations and tribulations of this life; the other which shall by then, and shall be spent in eternal security and joy. In figure of these, we celebrate two periods: the time before Easter, and the time after Easter. That which is before Easter signifies the sorrow of this present life; that which is after Easter, the blessedness of our future state... Hence it is that we spend the first in fasting and prayer; and in the second we give up our fasting, and give ourselves to praise.'
The Church, the intepreter of the sacred Scriptures, often speaks to us of two places, which correspond with these two times of St. Augustine. These two places are Babylon and Jerusalem. Babylon is the image of this world of sin, in the midst whereof the Christian has to spend his years of probation; Jerusalem is the heavenly country, where he is to repose after all his trials. The people of Israel, whose whole history is but one great type of the human race, was banished from Jerusalem and kept in bondage in Babylon.
Now, this captivity, which kept the Israelites exiles from Sion, lasted seventy years; and it is to express this mystery, as Alcuin, Amalarius, Ivo of Chartres, and all the great liturgists tell us, that the Church fixed the number of seventy for the days of expiation. It is true, there are but sixty-three days between Septuagesima and Easter; but the Church, according to the style so continually used in the sacred Scriptures, uses the round number instead of the literal and precise one.
The duration of the world itself, according to the ancient Christian tradition, is divided into seven ages. The human race must pass through the seven ages before the dawning of the day of eternal life. The first age included the time from the creation of Adam to Noah; the second begins with Noah and the renovation of the earth by the deluge, and ends with this the vocation of Abraham; the third opens with this first formation of God's chosen people, and continues as far as Moses, through whom God gave the Law; the fourth consists of the period between Moses and David, in whom the house of Juda received the kingly power; the fifth is formed of the years which passed between David's reign and the captivity of Babylon, inclusively; the sixth dates from the return of the Jews to Jerusalem, and takes us on as far as the birth of our Saviour. Then, finally, comes the seventh age; it starts with the rising of this merciful Redeemer, the Sun of justice, and is to continue till the dread coming of the Judge of the livng and the dead. These are the seven great divisions of time; after which, eternity.
In order to console us in the midst of the combats, which so thickly beset our path, the Church, like a beacon shining amidst the darkness of this our earthly abode, shows us another seven, which is to succeed the one we are now preparing to pass through. After the Septuagesima of mourning, we shall have the bright Easter with its seven weeks of gladness, foreshadowing the happiness and bliss of heaven. After having fasted with our Jesus, and suffered with Him, the day will come when we shall rise together with Him, and our hearts shall follow Him to the hightest heavesn; and then after a brief interval, we shall feel the Holy Ghost descending upon us, with His seven Gifts. The celebration of all these wondrous joys will take us seven weeks, as the great liturgists observe in their interpretation of the rites of the Church. The seven joyous weeks from Easter to Pentecost will not be too long for the future glad mysteries, which, after all, will be but figures of a still gladder future, the future of eternity.
Having heard these sweet whisperings of hope, let us now bravely face the realities brought before us by our dear mother the Church. We are sojourners upon this earth; we are exiles and captives in Babylon, that city which plots our ruin. If we love our country, if we long to return to it, we must be proof against the lying allurements of this strange land, and refuse the cup she proffers us, and with which she maddens so many of our fellow captives. She invites us to join in her feasts and her songs; but we must unstring our harps, and hang them on the willows that grow on her river's bank, till the signal be given for our return to Jerusalem. She will ask us to sing to her the melodies of our dear Sion: but how shall we, who are so far from home, have heart to 'sing the song of the Lord in a strange land'? No, there must be no sign that we are content to be in bondage, or we shall deserve to be slaves forever.
These are the sentiments wherewith the Church would inspire us during the penitential season which we are now beginning. She wishes us to reflect on the dangers that beset us; dangers which arise from ourselves and from creatures. During the rest of the year she loves to hear us chant the song of heavne, the sweet Alleluia; but now, she bids us close our lips to this word of joy, because we are in Babylon. We are pilgrims absent from our Lord, let us keep our glad hymn for the day of His return. We are sinners, and have but too often held fellowship with the world of God's enemies; let us become purified by repentance, for it is written that 'praise is unseemly in the mouth of a sinner.'
The leading feature, then, of Septuagesima, is the total suspension of the Alleluia, which is not to again be heard upon the earth until the arrival of that happy day, when having suffered death with our Jesus, and having been buried together with Him, we shall rise again with Him to a new life.
The sweet hymn of the angels, Gloria in excelsis Deo, which we have sung every Sunday since the birth of our Saviour in Bethlehem, is also taken from us; it is only on the feasts of the saints which may by kept during the week that we shall be allowed to repeat it. The night Office of the Sunday is to lose also, from now till Easter, its magnificent Ambrosian hymn, the Te Deum; and at the end of the holy Sacrifice, the deacon will no longer dismiss the faithful with his solemn Ite, Missa est, but will simply invite them to continue their prayers in silence, and bless the Lord, the God of mercy, who bears with us, notwithstanding all our sins.
After the Gradual of the Mass, instead of the thrice repeated Alleluia, which prepared our hearts to listen to the voice of God in the holy Gospel, we hsall hear but a mournful and protracted chant, called, on that account, the Tract.
That the eye, too, may teach us that the season we are entering on is one of mourning, the Church will vest her ministers (both on Sundays and on the days during the week which are not feasts of Saints) in the sombre purple. Until Ash Wednesday, however, she permits the deacon to wear his dalmatic, and the subdeacon his tunic; but from that day forward, they must lay aside these vestments of joy, for Lent will then have begun and our holy mother will inspire us with the deep spirit of penance, but suppressing everything of that glad pomp, which she loves at other seasons, to bring into the sanctuary of her God.